Patients sometimes present to ED or are send to ED due to over anticoagulation with warfarin
1. Is there Major/Significant bleeding?
Yes
- Resuscitate (ABCD)
- Give 5mg Vitamin K IV
- Octaplex Guide
- Treat bleeding and admit to appropriate speciality
Patients sometimes present to ED or are send to ED due to over anticoagulation with warfarin
 Cervical artery dissection is a rare but significant cause of stroke and headache/neckache, which is easy to overlook. Leading to a typically delay in diagnosis of 7 days. Unfortunately imaging the cervical arteries is not simple, with MRA being the method of choice. Hence these patients must be referred to the “Stroke Consultant”.
Cervical artery dissection is a rare but significant cause of stroke and headache/neckache, which is easy to overlook. Leading to a typically delay in diagnosis of 7 days. Unfortunately imaging the cervical arteries is not simple, with MRA being the method of choice. Hence these patients must be referred to the “Stroke Consultant”.
NHS England have published this fantastic resource [Click here] covering Major Incidents including; gunshot, crush, nerve agents and much more.
This is not to replace our trusts “Major Incident Plan”, however its a great learning resource and worth going through Read more
Adrenal crisis or insufficiency is a life threatening emergency due to the lack of glucocorticoid. Adrenal crisis can be primary due to destruction of the adrenal cortex (Addison’s), or secondary due to down regulation (chronic steroid use) Read more

For ALL conditions leading to bradycardia treating the underlying condition is the most appropriate treatment and for some the only thing that will work (i.e. severe hypothermia) Read more
Recent Incident: Bat contact was not recognized (effectively touching a bat without gloves means treatment is recommended)

Rabies is an acute viral encephalomyelitis caused by members of the lyssavirus genus. The UK has been declared “Rabies-Free”. However, it is known that even in “Rabies-Free” counties the bat population posse a risk.
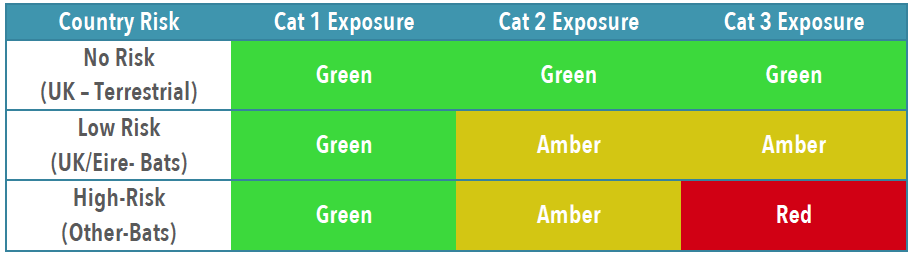
In the UK the only bat to carry rabies is the Daubenton’s Bat [Picture on the Left] and this is not a common bat in the UK. The UK and Ireland are Classified as “low-risk” for bat exposure. Despite our “low-risk” status in 2002 a man died from rabies caught in the UK from bat exposure.
Although rabies is rare it is fatal so we must treat appropriately, Public Health England – Green book details this.
To establish patients risk and thus treatment you need to establish the Exposure Category and Country Risk [Link to Country Risk]

Obviously patients with wounds will need appropriate wound care and cleaning, specifics for rabies are below.
If in ANY doubt, or you feel you need advice about treatment contact: On-Call Microbiologist (who will contact PHE or Virology advice)

You will likely need to liaise with the duty pharmacist to obtain vaccine or HRIG – which may need to be sent from a different hospital. [it is probably worth trying to obtain the 1st weeks treatment if possible, to avoid treatment delays]
IN HOURS 08:30AM-5PM PLEASE CALL PHARMACY TO INFORM THEM TO EXPECT A DELIVERY OF IMMUNOGLOBULIN SO THIS CAN BE SEGREGATED FOR THE CORRECT PATIENT. PLEASE ASK TO SPEAK TO THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST CRH (4218/4279) HRI (2422/7123)
Rabies and Immunoglobulin Service (RIgS), National Infection Service, Public Health England, Colindale (PHE Colindale Duty Doctor out of hours): 0208 327 6204 or 0208 200 4400
Vertigo is not always labyrinthitis!! There are some potentially serious conditions to think about. Your main question should be is it peripheral [good] or central [bad]?
Rhesus (Rh)-D negative women, pregnant with Rh-D positive foetus are at risk of developing antibodies against future pregnancies if/when they suffer a sensitising event. (Remember, this should be considered a standard treatment for all Rh-D negative women, as we are never certain of the fathers Rh-D status) Read more

Some Radial Buckle #’s in children can be managed with:
This decision tree must be followed to identify suitable patients
If you are concerned about Non-Accidental injury – you must escalate your concern.